Home Collection
STEP 1
Easy Online Booking
Select test, time, and address online.
STEP 2
Live Tracking
Track Phlebotomist In Real Time
STEP 3
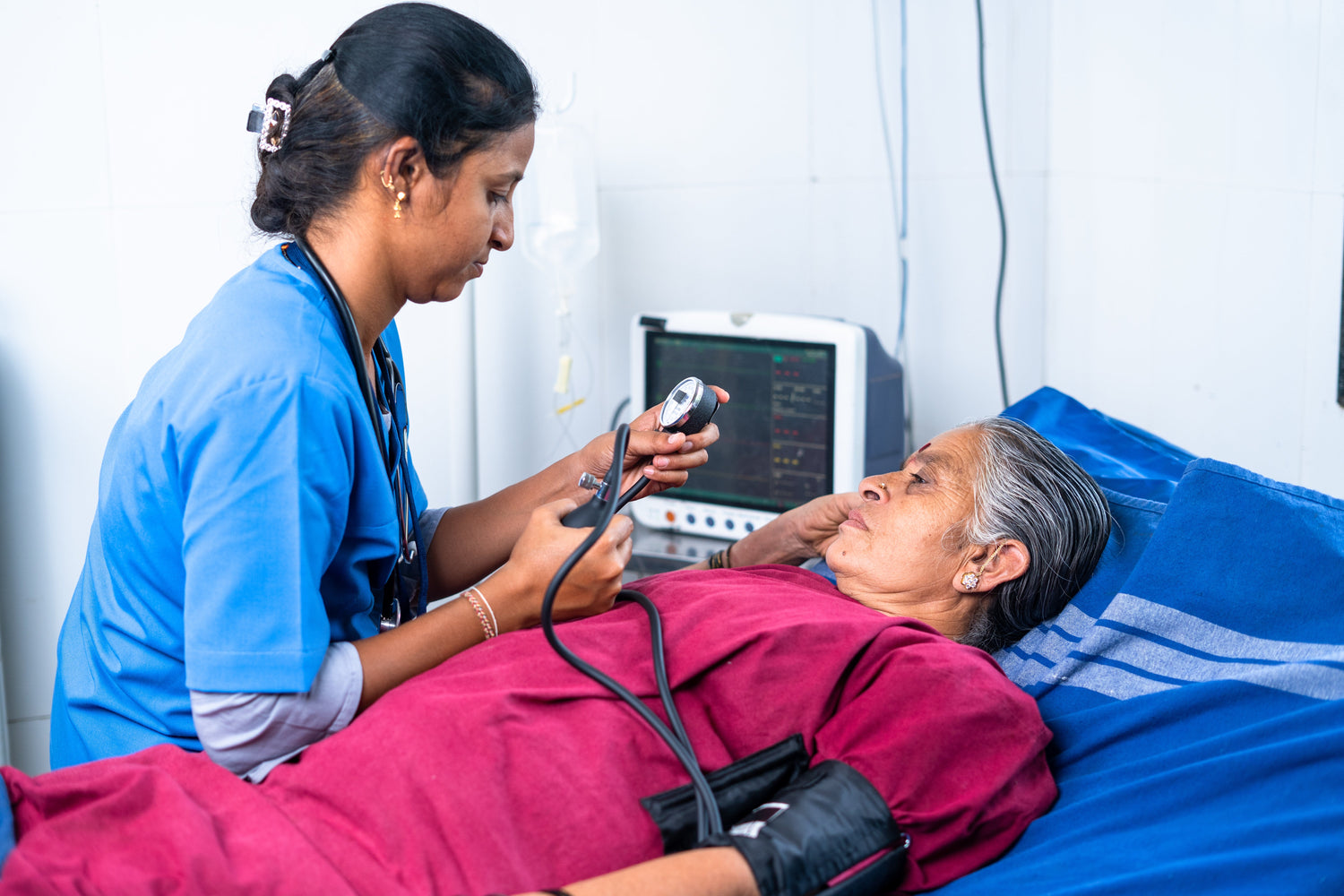
Safe Collection
Safe Sample Collection With Safety Protocols
STEP 4
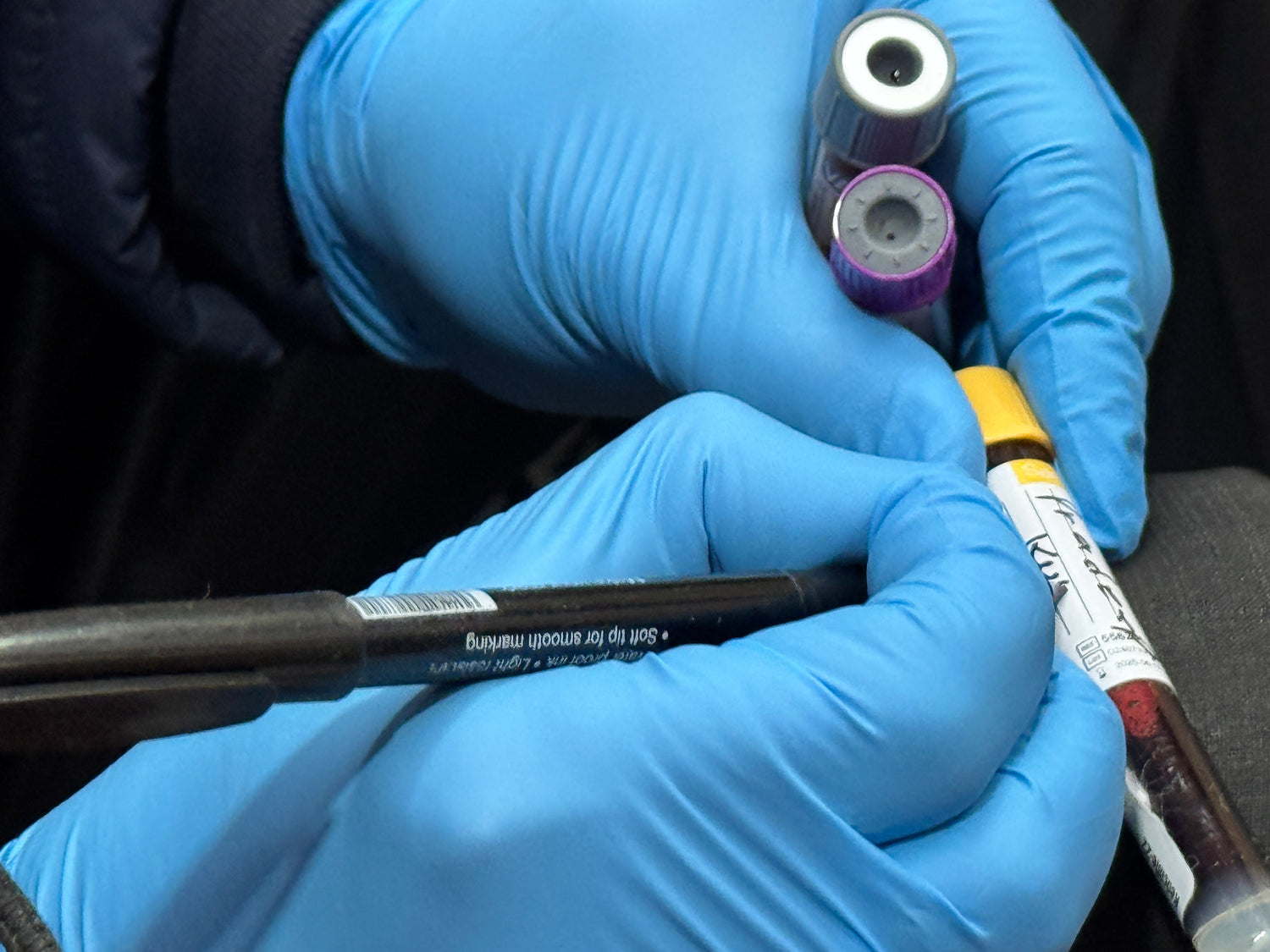
Lab Testing
Sample Sent To Certified Lab For Testing
STEP 5
Quick Reports
Get Reports By Email Or WhatsApp With Free Doctor Consultation
Frequently Asked Questions
The full form of HBV is Hepatitis B Virus.
This test measures the level of HBV DNA in the blood to check whether antiviral medicines are effectively reducing the viral load. Viral load monitoring helps doctors determine how well the treatment is working.
Pregnant women with HBV are screened for viral load. If the viral load is above 200,000 IU/mL, antiviral therapy is recommended in the third trimester to reduce the risk of passing the infection to the baby.
Yes. Breastfeeding is usually safe if the baby has received the complete hepatitis B vaccine series and HBIG at birth. HBV is not transmitted through breast milk.
No, it is not primarily a diagnostic test. It is used to monitor people already diagnosed with hepatitis B. Initial diagnosis is done using other HBV tests such as HBsAg, anti-HBc, etc.
It means the amount of virus in the blood is too low to be measured. This usually indicates inactive infection or successful response to treatment.
Common symptoms include: Fatigue Muscle/joint pain Loss of appetite Dark urine Fever Abdominal pain Jaundice (yellow skin/eyes)
Symptoms may appear 8 weeks to 5 months after exposure, typically around 90 days (3 months).
Hepatitis B spreads through: Unprotected sex Sharing needles/syringes Mother-to-baby transmission at birth Sharing personal items (razors, toothbrushes) Unsafe tattooing or piercing
No. HBV does not spread through food, water, utensils, hugging, kissing, handshakes, coughing, or sneezing.
Acute infection: infectious for weeks to up to 6 months Chronic infection: infectious lifelong, with a risk of liver cirrhosis or cancer
Prevention includes: Hepatitis B vaccination (0, 1, and 6 months) Practicing safe sex Avoiding direct contact with blood Not sharing needles Ensuring safe tattoo/piercing practices Maintaining proper hygiene
The major hepatitis viruses are: Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E