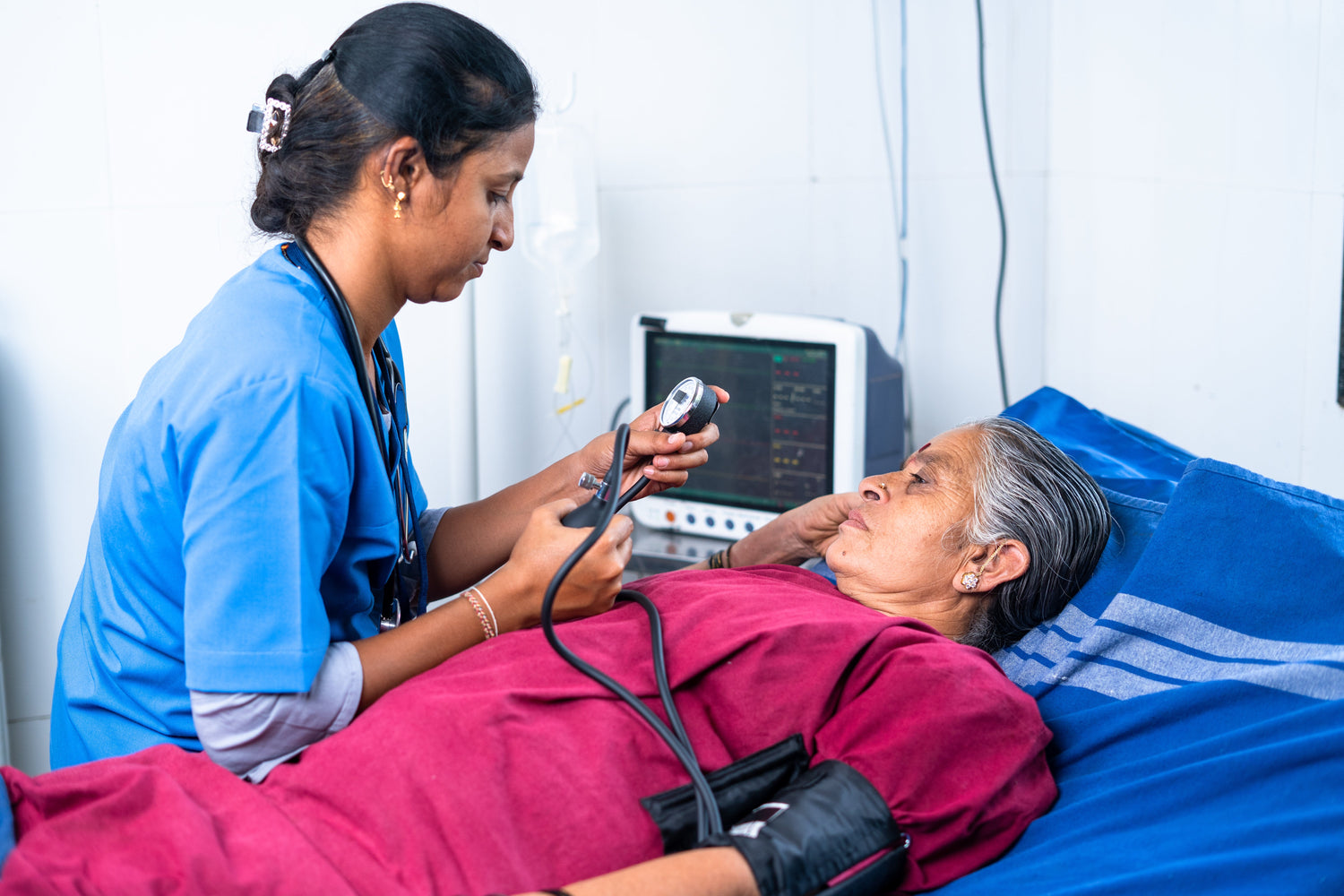
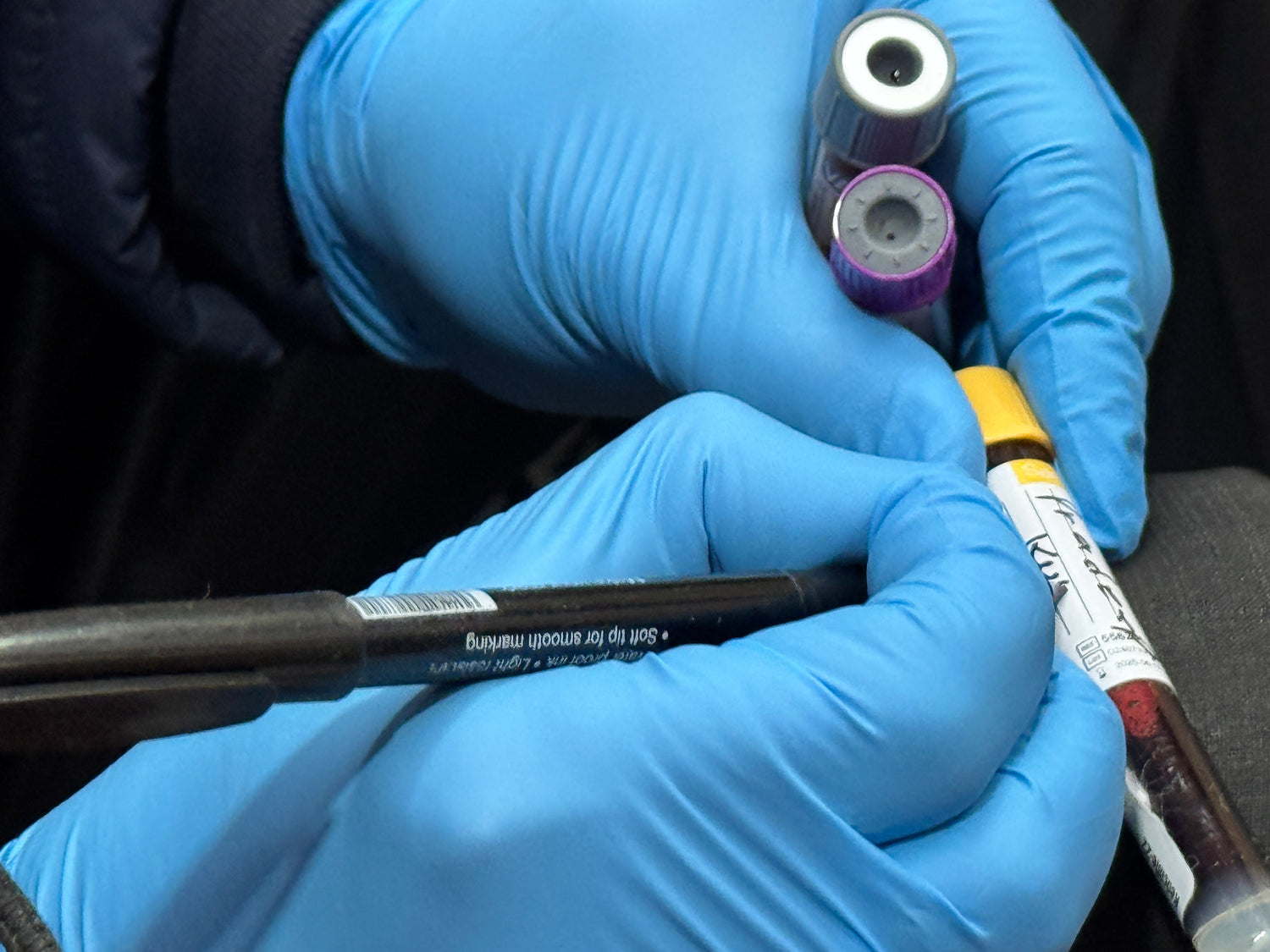
Curebay Premium Diabetes Care Package
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most pressing health challenges of the 21st century.
Sample Required
🩸 Blood, Urine
This test is for
👤 Male,Female
Earliest reports in
⏱ 24 hours
Contains
🧪 13 tests
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG)
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
- HbA1c
- Random Plasma Glucose (RPG)
- Lipid Profile
- Liver Function Test (LFT)
- Kidney Function Test (KFT)
- Complete Hemogram
- RBS/FBS
- Eye Examination
- Foot Examination
- Blood Pressure Measurement
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) / SMBG
Method Name
🧬 Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) – Enzymatic Colorimetric Method, OGTT – Glucose Oxidase/Hexokinase Method, HbA1c – HPLC / Immunoassay Method, Lipid Profile – Enzymatic Assay, LFT – Photometric Method, KFT – Enzymatic & Colorimetric Method, Complete Hemogram – Automated Cell Counter, RBS/FBS – Glucose Oxidase Peroxidase Method
Preparations Required
- ✓ 8–10 hrs fasting required Avoid high sugar meals before test
Know more about this test
A comprehensive diabetes screening and monitoring test package helps identify diabetes, prediabetes, and related complications at an early stage. It combines... A comprehensive diabetes screening and monitoring test package helps identify diabetes, prediabetes, and related complications at an early stage. It combines multiple assessments, including blood glucose tests, HbA1c, lipid profile, kidney and liver function tests, and physical examinations. This package plays an essential role in early diagnosis, continuous monitoring, and prevention of long-term complications such as kidney failure, nerve damage, vision loss, and heart disease. It also guides treatment decisions, lifestyle modification, and timely intervention to maintain long-term health. see more
Understanding Curebay Premium Diabetes Care Package
What is Curebay Premium Diabetes Care Package
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most pressing health challenges of the 21st century. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), more... Diabetes mellitus is one of the most pressing health challenges of the 21st century. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), more than 537 million adults worldwide are living with diabetes in 2021, and this number is projected to rise to 643 million by 2030 and 783 million by 2045. In India alone, the number of people with diabetes is estimated at over 77 million, making it the diabetes capital of the world. The chronic nature of diabetes, its silent onset, and its complications—ranging from cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, blindness, to amputations—highlight the need for a structured, comprehensive package of screening and monitoring. Unlike acute illnesses, diabetes requires lifelong surveillance, not only for glycemic control but also for prevention and early detection of complications. A well-designed diabetes screening and monitoring package ensures early diagnosis, risk stratification, timely intervention, and regular follow-up. It combines medical, technological, and lifestyle components into a holistic framework that improves patient outcomes, reduces healthcare costs, and enhances quality of life. Objectives of a Comprehensive Package A structured package for diabetes screening and monitoring should aim to: Detect undiagnosed diabetes and prediabetes in high-risk populations. Identify comorbidities like hypertension, dyslipidemia, and obesity. Monitor glycemic status and assess effectiveness of treatment. Detect early complications involving eyes, kidneys, nerves, and heart. Provide lifestyle modification support—nutrition, physical activity, stress management. Incorporate technological tools for real-time monitoring and adherence. Ensure cost-effectiveness and accessibility for urban and rural populations. Target Population for Screening Screening is essential because diabetes often remains undiagnosed until complications develop. The following groups should be prioritized: General adult population: All adults ≥35 years should undergo baseline screening. High-risk individuals (any age): Family history of diabetes (first-degree relative). Overweight/obesity (BMI ≥23 kg/m² in Asians). Sedentary lifestyle. Hypertension, dyslipidemia, or cardiovascular disease. History of gestational diabetes or delivering a baby >4 kg. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). Children and adolescents: Overweight children with ≥2 risk factors (family history, ethnicity, maternal history, obesity-related comorbidities). Components of Screening 1. Risk Assessment Questionnaire-based tools such as the Indian Diabetes Risk Score (IDRS), FINDRISC, or ADA risk calculator. Parameters include age, BMI, waist circumference, physical activity, family history, and hypertension. 2. Clinical Examination Measurement of BMI, waist-to-hip ratio, and blood pressure. Signs of insulin resistance: acanthosis nigricans, skin tags, central obesity. 3. Laboratory Investigations Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG): ≥126 mg/dL diagnostic. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): 2-hr plasma glucose ≥200 mg/dL diagnostic. HbA1c: ≥6.5% diagnostic; also useful for monitoring. Random Plasma Glucose: ≥200 mg/dL with classic symptoms. Diagnostic Criteria (ADA/WHO/ICMR Guidelines) Test Normal Prediabetes Diabetes FPG <100 mg/dL 100–125 mg/dL ≥126 mg/dL OGTT (2hr) <140 mg/dL 140–199 mg/dL ≥200 mg/dL HbA1c <5.7% 5.7–6.4% ≥6.5% Diagnosis should be confirmed with repeat testing unless unequivocal hyperglycemia is present. Monitoring Parameters Monitoring goes beyond just blood sugar checks. A comprehensive package should include: 1. Glycemic Monitoring Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG): Fasting, pre-meal, post-meal, bedtime. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Provides trends, hypoglycemia detection, glucose variability. HbA1c (every 3–6 months): Long-term control marker. Target usually <7%. 2. Metabolic Monitoring Lipid profile (annually, more frequently if uncontrolled). Blood pressure monitoring (every visit). Weight, BMI, waist circumference (monthly). 3. Organ-Specific Monitoring Eyes: Fundus examination/retinal photography annually. Kidneys: Urine albumin-creatinine ratio, eGFR yearly. Nerves: Foot examination (monofilament, vibration sense) annually. Heart: ECG and cardiovascular risk assessment every 1–2 years. 4. Lifestyle & Psychosocial Monitoring Diet adherence and nutritional counseling. Physical activity tracking (pedometers, fitness apps). Stress, sleep, and mental health assessment. Technological Aids in Monitoring Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM): Real-time insights, useful for insulin-dependent diabetics. Smartphone Applications: Diet logging, reminders, doctor-patient communication. Telemedicine: Remote consultations, especially for rural patients. Wearables: Track activity, sleep, and calorie expenditure. Frequency of Screening & Monitoring At-risk but non-diabetic individuals: Every 3 years. Prediabetes: Annually. Diabetes: HbA1c: Every 3–6 months. Lipid profile: Annually. Renal, eye, and nerve screening: Annually. Foot check: At every visit. Integration with Lifestyle, Diet, and Exercise Plans A comprehensive package must go beyond diagnosis to include preventive and therapeutic lifestyle changes: Nutrition: Personalized diet plans emphasizing low glycemic index foods, fiber, portion control, and reduced refined sugars. Exercise: At least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week + resistance training twice weekly. Behavioral Support: Counseling for stress management, smoking cessation, and alcohol moderation. Cost-Effectiveness & Accessibility Using risk scores and basic tests (FPG, HbA1c) for mass screening is cost-effective. Community-based programs, health camps, and integration into primary healthcare systems make screening more accessible. Insurance packages and government schemes (like Ayushman Bharat) can cover essential monitoring. Challenges in Implementation Awareness gap – Many remain undiagnosed until complications appear. Healthcare infrastructure – Rural areas lack diagnostic facilities. Cost of monitoring devices – CGM and insulin pumps are expensive. Patient adherence – Lifestyle changes are difficult to sustain. Fragmented care – Lack of integrated multidisciplinary teams. read more
Why These Tests Are Used in Diabetes Screening & Monitoring
1. Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) Why used: Measures blood sugar after at least 8 hours of fasting. Purpose: Detects impaired fasting glucose a... 1. Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) Why used: Measures blood sugar after at least 8 hours of fasting. Purpose: Detects impaired fasting glucose and diabetes at an early stage. It is simple, cost-effective, and widely available. 2. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) Why used: Measures body’s response to a fixed glucose load (usually 75 g). Purpose: Gold standard for diagnosing prediabetes and diabetes. Useful in detecting cases that fasting glucose might miss (especially post-meal hyperglycemia). 3. HbA1c (Glycated Hemoglobin) Why used: Reflects the average blood glucose over the past 2–3 months. Purpose: Long-term glycemic control monitoring; helps assess how effective treatment is. Doesn’t require fasting. 4. Random Plasma Glucose (RPG) Why used: Can be done anytime, regardless of meals. Purpose: Useful in symptomatic patients (polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss) where diabetes can be diagnosed if ≥200 mg/dL. 5. Lipid Profile Why used: Measures cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Purpose: Diabetes often coexists with dyslipidemia, increasing cardiovascular risk. Monitoring lipids helps prevent heart disease. 6. Blood Pressure Measurement Why used: High blood pressure is common in diabetics. Purpose: Detects and prevents cardiovascular and kidney complications. 7. Kidney Function Tests (Serum Creatinine, eGFR, Urine Albumin-Creatinine Ratio) Why used: To check kidney function. Purpose: Detects diabetic nephropathy early, even before symptoms appear. 8. Eye Examination (Fundus/Retinal Photography) Why used: Diabetes damages tiny blood vessels in the retina. Purpose: Detects diabetic retinopathy early to prevent blindness. 9. Foot Examination (Monofilament, Vibration Sense) Why used: Tests for nerve damage and poor circulation. Purpose: Prevents diabetic foot ulcers and amputations. 10. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) / Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG) Why used: Tracks daily fluctuations in blood sugar. Purpose: Helps patients and doctors adjust medication, diet, and insulin for tighter control. read more
- Risk Assessment
- Clinical Examination
- Laboratory Investigations
- Glycemic Monitoring
- Metabolic Monitoring
- Organ-Specific Monitoring
- Lifestyle & Psychosocial Monitoring
- Technological Tools (CGM, Apps, Telemedicine)
What Each Test Measures

Home Collection

STEP 1
Easy Online Booking
Select test, time, and address online.
STEP 2
Live Tracking
Track Phlebotomist In Real Time

STEP 3
Safe Collection
Safe Sample Collection With Safety Protocols

STEP 4
Lab Testing
Sample Sent To Certified Lab For Testing

STEP 5
Quick Reports
Get Reports By Email Or WhatsApp With Free Doctor Consultation
Frequently Asked Questions
Take medications as prescribed unless told otherwise by your physician.
Every 3-6 months if diabetic.
Save more with recommended Tests/Packages
Answers You Need, Experiences You Can Trust
Answers You Need, Experiences You Can Trust
Answers You Need, Experiences You Can Trust
Answers You Need, Experiences You Can Trust
FAQs
SEE ALL FAQS
What are CureBay Health Packages?
CureBay Health Packages are a combination of essential diagnostic tests and preventive checkups, designed to monitor overall health and detect potential issues early.
How can I book a package?
You can easily book through CureBay’s website, mobile app, or helpline. Once booked, you’ll receive confirmation and a phlebotomist will be scheduled for home sample collection.
Can I book tests for my family members?
That depends on the supplement and your personal health goals. The results are visible depending on your consistency. Remember to be consistent to feel a noticeable difference.
How will I get my reports?
Reports are delivered digitally within the mentioned TAT (Turnaround Time) via Email, WhatsApp, and CureBay’s platform.
Are doctor consultations included in the packages?
Many packages include complimentary doctor consultations to help you understand your test results and guide next steps for better care.
Customer Reviews
-
We booked CureBay’s Corporate Health Package for our staff at Techzone, and the experience was outstanding.
 Snigdha MandalHR Manager
Snigdha MandalHR Manager -
I booked a health package with CureBay for my family, and I am very satisfied with their service. The home sample collection was hassle-free, and the reports came quickly with clear guidance from doctors.
 Mamali MohantyHome Maker
Mamali MohantyHome Maker -
I recently booked a diagnostic test with CureBay, and I must say the service was excellent.
 Harihar MohapatraSchool Teacher
Harihar MohapatraSchool Teacher

Curebay Premium Diabetes Care Package
-

Home Sample Collection
-

NABL-Certified Partner Labs
-

First & Accurate Report
-

Digital Report Access