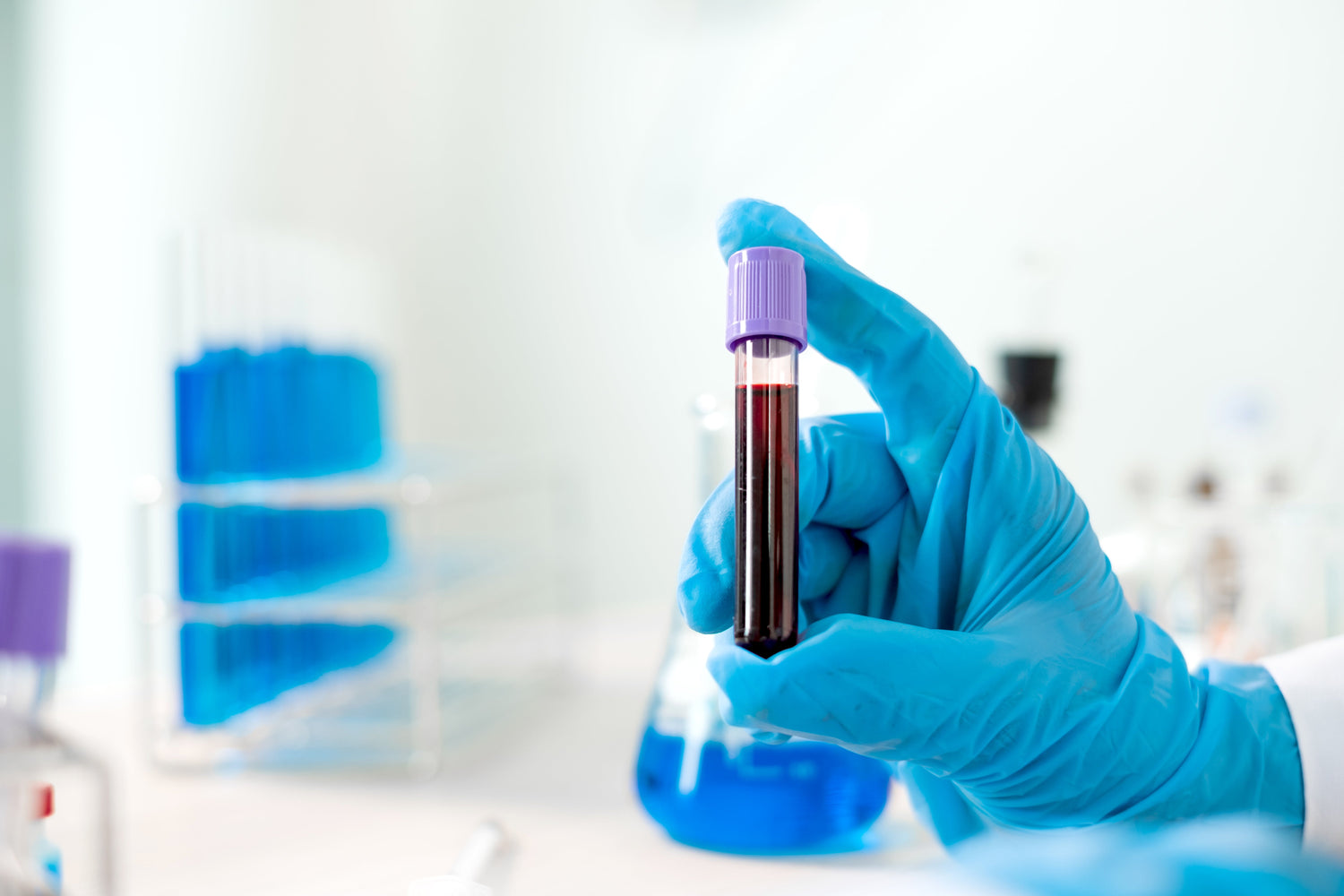
Home Collection
STEP 1
Easy Online Booking
Select test, time, and address online.
STEP 2
Live Tracking
Track Phlebotomist In Real Time
STEP 3
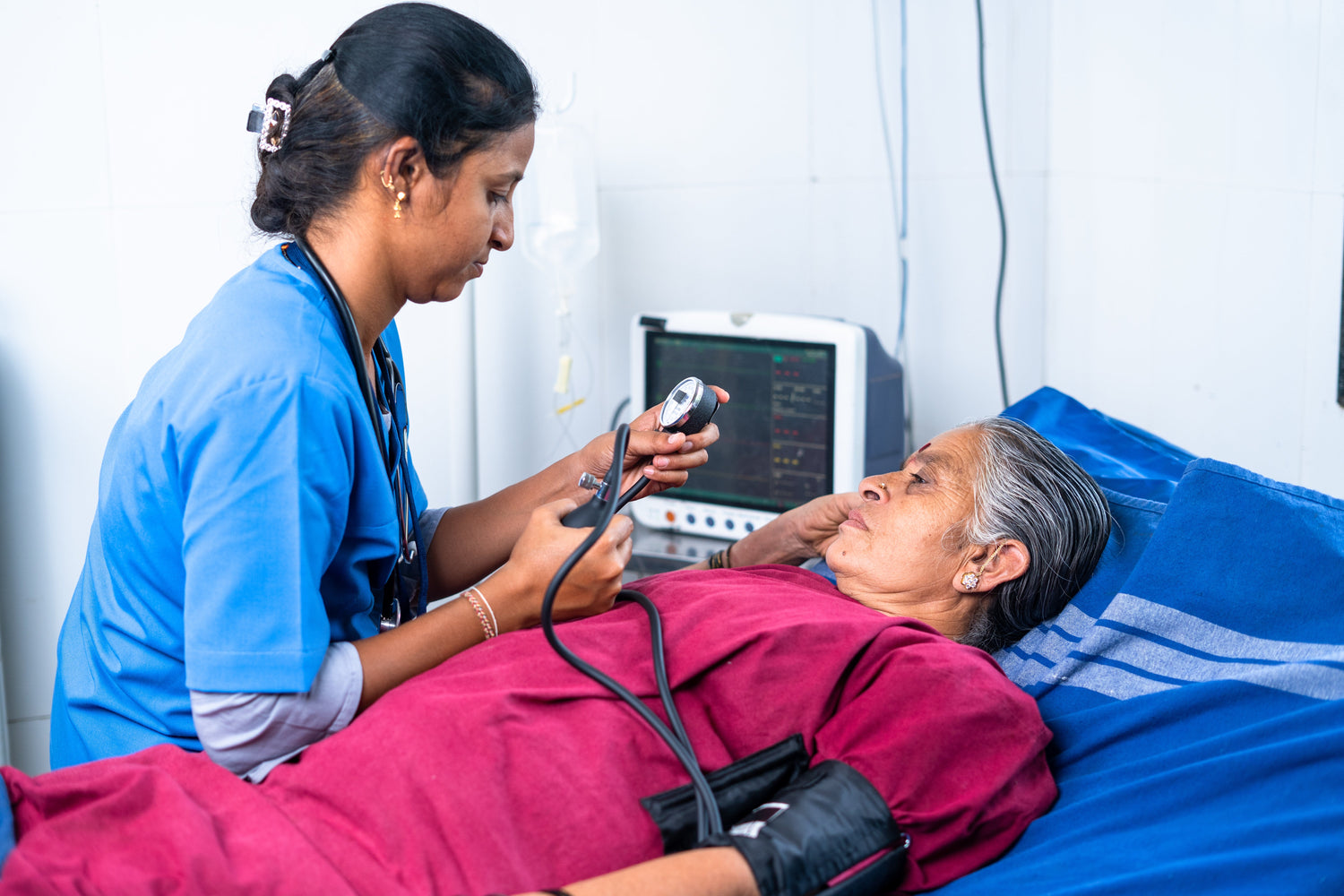
Safe Collection
Safe Sample Collection With Safety Protocols
STEP 4
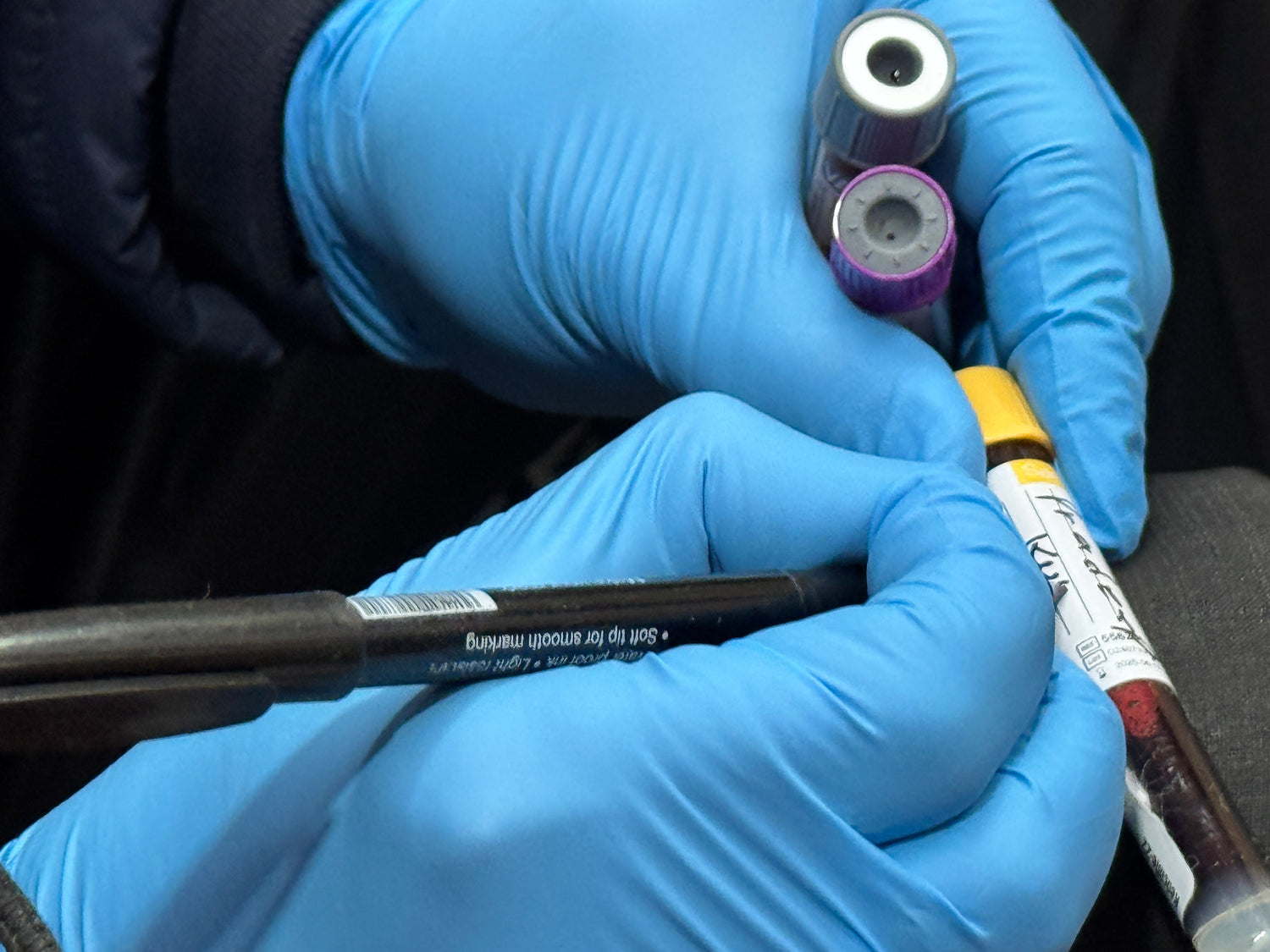
Lab Testing
Sample Sent To Certified Lab For Testing
STEP 5
Quick Reports
Get Reports By Email Or WhatsApp With Free Doctor Consultation
Frequently Asked Questions
An AMH test is used to assess ovarian reserve and fertility potential, diagnose PCOS, menstrual irregularities, and guide pregnancy or fertility planning.
A phlebotomist draws a blood sample from a vein using a sterile needle, which is then sent to the laboratory for analysis.
Yes, the AMH test can be taken any day of the menstrual cycle because AMH levels remain stable throughout the month.
High AMH levels may indicate PCOS or a higher risk of ovarian hyperstimulation during fertility treatments. In males, abnormal AMH levels may relate to fertility issues.
Low AMH levels indicate reduced ovarian reserve and may suggest early menopause or lower fertility potential.
Yes, men can also undergo AMH testing, although it is more commonly used in women for fertility evaluation.
In males, AMH suppresses the development of Müllerian ducts during fetal development, ensuring normal male reproductive organ formation.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle—regular exercise, balanced diet, good sleep, weight management, and stress control—may help improve AMH levels naturally.
Estradiol test, FSH test, chromosomal analysis, and pelvic ultrasound can be performed along with an AMH test.
There is no guaranteed way to increase AMH significantly, but healthy habits like proper diet, exercise, and avoiding smoking may help maintain reproductive health.
A good AMH level for pregnancy varies with age. Higher AMH suggests better ovarian reserve, but fertility depends on many factors, not AMH alone.
The cost of the AMH test varies depending on location, lab type, and whether it is part of a fertility panel.
Low AMH means reduced ovarian reserve, which can make conception more difficult.
Foods rich in vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, fiber, and plant proteins may support overall reproductive health.